One can broadly define vulnerability management as a set of processes and procedures to identify, analyze, and manage vulnerabilities across a critical service's operating environment.
This broad definition extends to IT systems and infrastructure, which are now as critical as power generation facilities and resource gathering operations. Keeping in mind the growing number and sophistication of cyber-attacks against organizations of all sizes and across any industry vertical, any enterprise should have a program to detect and proactively reduce risks associated with cybersecurity.
Today's best practices for vulnerability management require organizations to continuously scan for vulnerabilities in their systems instead of the historical approach of performing a vulnerability scan once in a half year or less often. The cyber-threats environment is a fast-developing one and requires organizations to take a holistic view if they are to make informed decisions about the most critical vulnerabilities and remediate the risks originating from such vulnerabilities.
All definitions, including one by the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA), divide the vulnerability management process into four stages, as shown below:
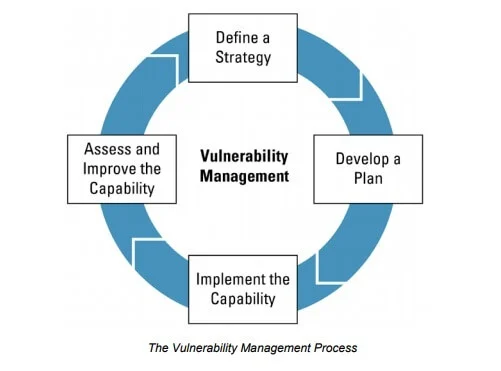
Source: CISA
As you can see, the above definition is all about strategy and not patching specific kinds of vulnerabilities as you can have weak points in any computing system or one of their infrastructural components. Thus, we can say that vulnerability management is a critical component in planning for the appropriate implementation of controls and the management of risks associated with cybersecurity.
Vulnerability management is often confused with software patching and vulnerability scanning. While scanning for vulnerabilities and patching them are critical components of vulnerability management, it is more of a concept and an action plan for detecting and remediating cybersecurity risks and threats.
Such a complex strategy cannot be run manually, and that is why organizations implement sophisticated tools to scan for vulnerabilities across their business-critical IT systems. Those automated tools can detect various vulnerabilities and take automated actions to remediate the risk or generate alerts for the organization's IT team.
A report by the SANS Institute shows that 85 percent of the organizations surveyed worldwide say they are running automated tools for vulnerability management.
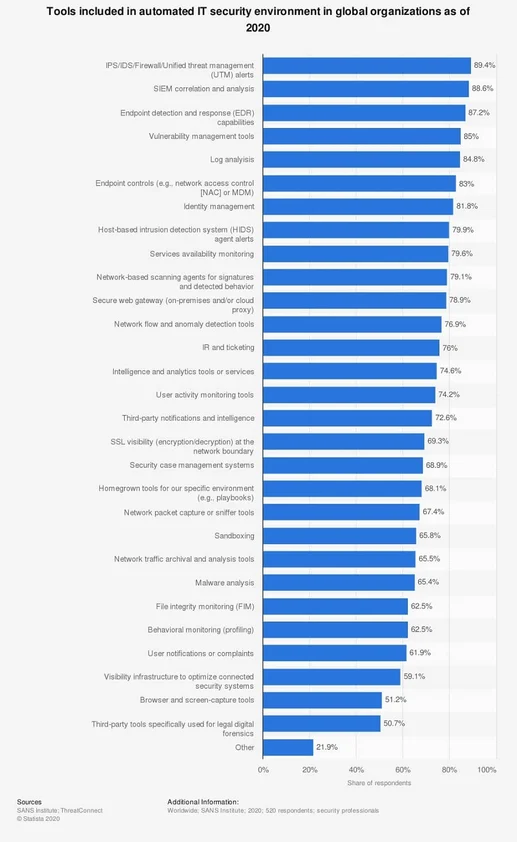
Source: Statista
There is no abundance of vulnerability scanners on the market as cybersecurity is one of the most rapidly growing IT industry markets. Proprietary and open-source vulnerability scanners offer a collection of cybersecurity tools and features such as:
You can find even more features in advanced vulnerability scanning software by known vendors such as IBM or McAfee. The list of reliable vulnerability scanners can be extended to include:
With so many products on the market, organizations should carefully assess each vulnerability scanner's capabilities before deciding on adopting it. Furthermore, different vulnerability scanners can produce very different results while scanning the same resource or network.
You cannot rely solely on vulnerability scanners for your cybersecurity defenses, as you need a holistic approach that combines passive and active protection, including research and remediation against unknown threats.
Furthermore, the vulnerability management process extends beyond scanning for cybersecurity gaps and involves automated and manual actions to respond, quarantine, and remediate known and unknown threats targeting your organization's IT ecosystem.
We can start by providing a more complex definition of how the vulnerability management process works. We have already mentioned that there are four phases of vulnerability management:
You can rescan as a component of the process, but it belongs to the vulnerability management process's research and plan stage.
Below, you can see how the entire process works by combining automation and manual vulnerability response actions.
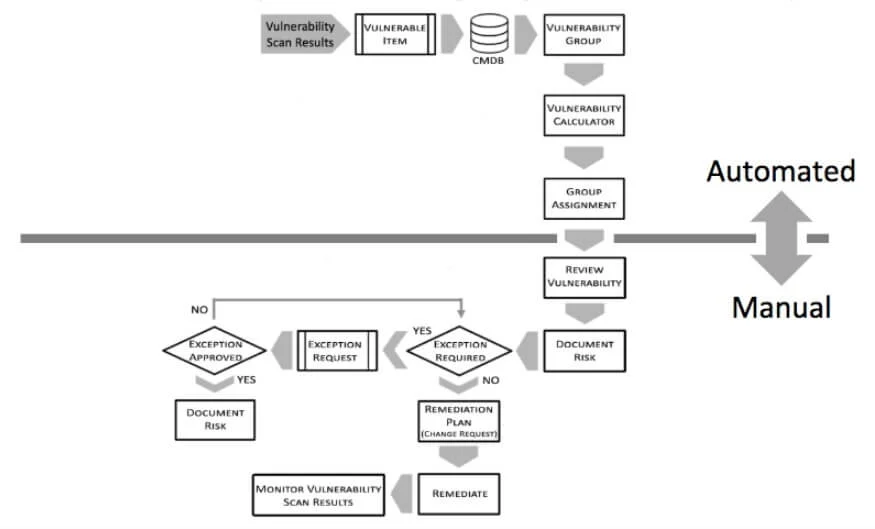
Source: ServiceNow
The above chart represents the vulnerability management process in action, and now we will focus on the individual stages through which the process goes.
During the preparation and research phase, your security team defines the scope of the vulnerability management process. That being said, a recommended approach is to start small – by scanning a few selected systems and parts of the network – before you proceed with complex scans of your entire IT infrastructure.
Your teams should also agree on which systems and endpoints will be included in the vulnerability scanning process and excluded, regardless of the reasoning behind such a decision.
In any case, you should plan for external scanning to be performed to get visibility about how your cyber defenses look like from the outside. It means that you need to prepare for internal and external scanning and define the scans' exact scope to be conducted.
Your organization should cover as many assets as possible because limiting the vulnerability scanning scope may result in leaving critical security gaps unaddressed.
After an organization had completed the planning stage, the time comes to run the actual scans for vulnerabilities within the context of the defined scope and types of vulnerabilities to be detected.
During this stage, your cybersecurity team needs to identify the overall number of vulnerabilities across the organization's systems and determine the severity of risks associated with those vulnerabilities.
While you are running scans on your selected IT systems, you can also identify which endpoints and networked components are experiencing excessive loads and take actions to prevent eventual overloading in the future.
Once the organization's cybersecurity team had analyzed the detected vulnerabilities across the tested systems, they need to plan for and define which remediation actions will be taken in each case. The process involves deciding whether patches will be applied or specific systems will be reconfigured to remove the vulnerabilities.
All risks need prioritization, especially if there is no immediate solution to a specific vulnerability due to patches not being available or specific system configuration requirements.
Implementing remediation actions should follow a strict procedure in which all detected vulnerabilities are being patched following the drafted vulnerability management action plan.
In implementing the planned remediation actions, your team needs to define alternative steps and procedures where the planned actions prove to be ineffective.
The organization's cybersecurity team completes the process by rescanning the systems included in the vulnerability management process to ensure all risks are mitigated, and no known vulnerabilities are left unpatched.
The rescanning process should be continuous if your organization wants to maintain an acceptable level of protection against hackers being able to exploit known and possible vulnerabilities.
The vulnerability management process is very complex and may involve thousands of machines to scan for existing vulnerabilities and secure against newly emerging vulnerabilities. While an organization running a network of less than a dozen computing devices can cope with vulnerability management challenges, adopting an enterprise-grade process for vulnerability management is usually impossible without having a dedicated team of cybersecurity experts.
One possible solution is to conduct thorough research for a vulnerability-scanning platform that best suits the needs of the organization and then contact a managed security services provider (MSSP) who can implement and maintain the solution in the long run.
The number of vulnerability scans required to complete on hundreds of in-house machines and cloud-based assets is beyond the average organization's capability. Furthermore, hundreds of specific settings can configure and adjust for the vulnerability management process to produce feasible results, so assistance by an expert MSSP is more than advantageous at any stage of the vulnerability management process.
Lumifi has helped organizations create and improve their vulnerability management programs.
